 Saline infusion sonohysterography (SIS) is also sometimes called saline infusion hysterogram (SHG). It is an investigative procedure to assess the uterus cavity to ascertain the shape and look for any abnormalities within it. It incorporates an ultrasound scan and instillation of sterile fluid into the uterus to show the uterine cavity and endometrial layers. With the use of an ultrasound scan, the uterine wall and the ovaries can be visualized as well.
Saline infusion sonohysterography (SIS) is also sometimes called saline infusion hysterogram (SHG). It is an investigative procedure to assess the uterus cavity to ascertain the shape and look for any abnormalities within it. It incorporates an ultrasound scan and instillation of sterile fluid into the uterus to show the uterine cavity and endometrial layers. With the use of an ultrasound scan, the uterine wall and the ovaries can be visualized as well.
Reasons for the SIS
SIS is indicated when a woman has the following conditions:
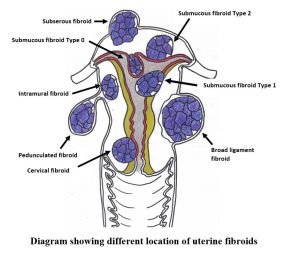
- abnormal uterine bleeding which may be due to an intrauterine growth such as submucous fibroids or endometrial polyps.
- further assessment in women with difficulty in conceiving or recurrent miscarriages, when there is a suspicion that these problems may be due to an abnormality within the uterine cavity.
- to rule out congenital abnormalities (birth defects) of the uterus or the presence of scar tissue.
SIS should not be done in women who are either pregnant or who are suspected to be pregnant and those with an ongoing active vagina or pelvic infection.
Preparation for SIS
- SIS is usually scheduled right after menses. This is the ideal time because following menses, the endometrium layers will be thin and any structural abnormalities in the uterine cavity can be easily seen. In women who are not menstruating (either on medication for menstrual suppression or after menopause), the SIS can be scheduled at any time. Please discuss this with your doctor if you are unsure or if you suspect that you may be pregnant.

- If you have abnormal vaginal discharge, please inform your doctor. The procedure should be deferred until the infection has been ruled out or has been adequately treated.
- No fasting is required. However, it is not advisable to take a full meal just prior to the procedure.
- Oral pain-killer medications may be given one hour prior to the procedure. This will help to reduce the crampy pain. Additional doses may be given for you to take home. Please follow the instructions carefully when taking these medications.
- Please schedule an appointment for this procedure once your menstrual flow starts. This is to enable the doctor to schedule it right after menses.
- Please abstain from unprotected sexual intercourse before the procedure or use a safe method such as condoms.
How is SIS done?
- The procedure is quick; usually takes about 15 to 20 minutes from start to finish.
- No specific anaesthesia is required. You will be conscious during the procedure and can view the image on the screen.
- A preliminary ultrasound scan of the uterus with a trans-vaginal probe may be done first.
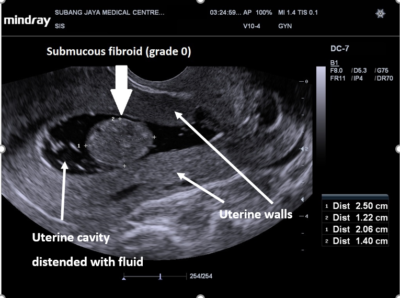
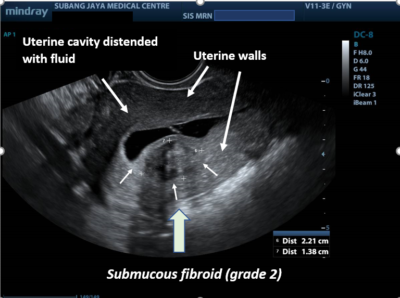
A speculum is inserted into the vagina and the cervix is visualized. The cervix and vagina are clean with an antiseptic. - A disposable balloon catheter is inserted into the uterine cavity and sterile saline is slowly inserted into the uterus. At the same time, the ultrasound scan is continued while the sterile saline is slowly injected into the uterus. The saline fluid will distend the uterine cavity and outline the shape and any other abnormal structures within it. It can show the presence of submucous fibroids, endometrial polyps, scar tissues or abnormal endometrial layers (such as thickening).
- There may be some cramping or discomfort felt as the fluid is injected.
- The findings will be available immediately and discussed with you.
Below are SIS scan pictures showing normal intrauterine cavities, submucous fibroid, and endometrial polyp.
Post-procedure care
- Mild cramping pain, a slow pulse, some nausea, or dizziness may occur during or following the procedure. These are temporary.
- Expect some vaginal spotting after the procedure but no heavy vaginal bleeding. Also, the solution used to clean the vagina and cervix and some of the dye itself will leak out through the vagina after the procedure. Wear a sanitary napkin for one or two days.
- Following the procedure, painkillers medications can be continued if the crampy pain is present.
- There are no dietary or activity restrictions once any temporary symptoms disappear.
- Most women will be able to drive safely after resting for one hour following the SIS and when there is no significant discomfort. You may return to work soon after if you are well.
Possible complications
It is a very safe procedure and serious complications are rare. Possible complications are:
- infection which is usually due to co-existing infections in the fallopian tubes or pelvis. This can be treated with antibiotics.
- uterine cramps for several hours and can be relieved with oral pain-killer medication.
See your doctor immediately if you have:
- Increased pain in the lower abdomen or in the genital area over the next 24 to 48 hours.
- Signs of infection: headache, muscle aches, dizziness or general ill feeling, and fever.
- Persistent or heavy vaginal bleeding.
- Persistent and abnormal vaginal discharge.
To print a pdf copy, click HERE
To watch videos of SIS, click the link below:
Gynaecology video page OR
Video 1, Video 2, Video 3, Video 4
[mailerlite_form form_id=3]