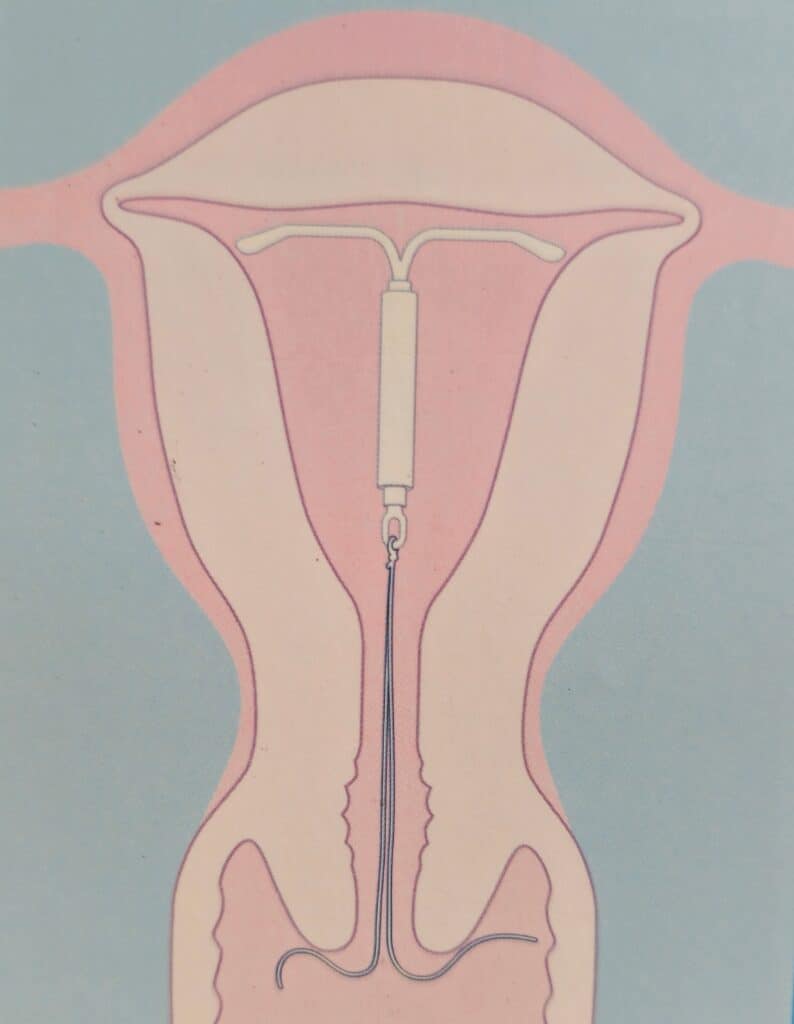
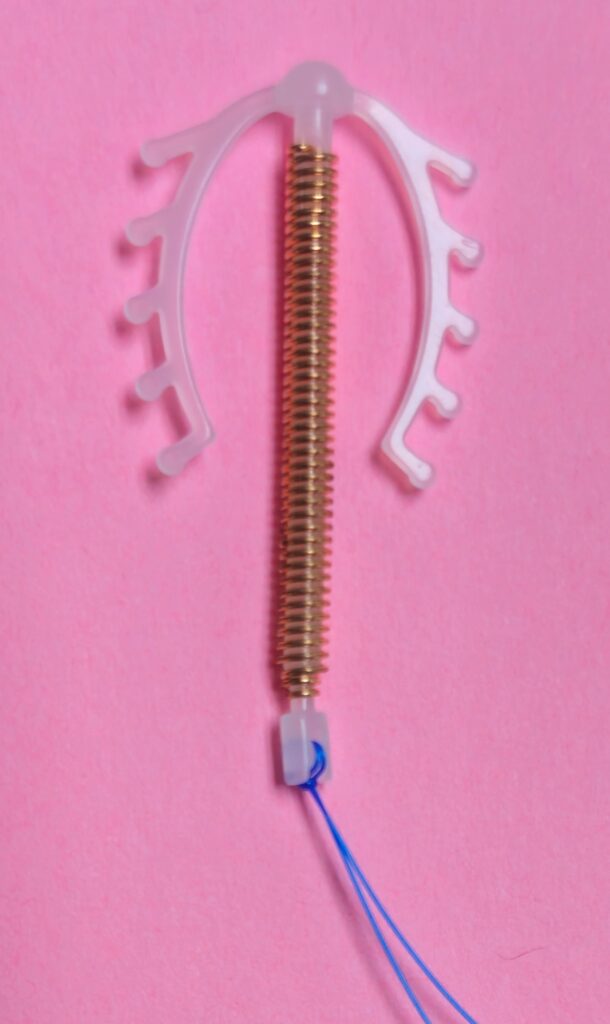
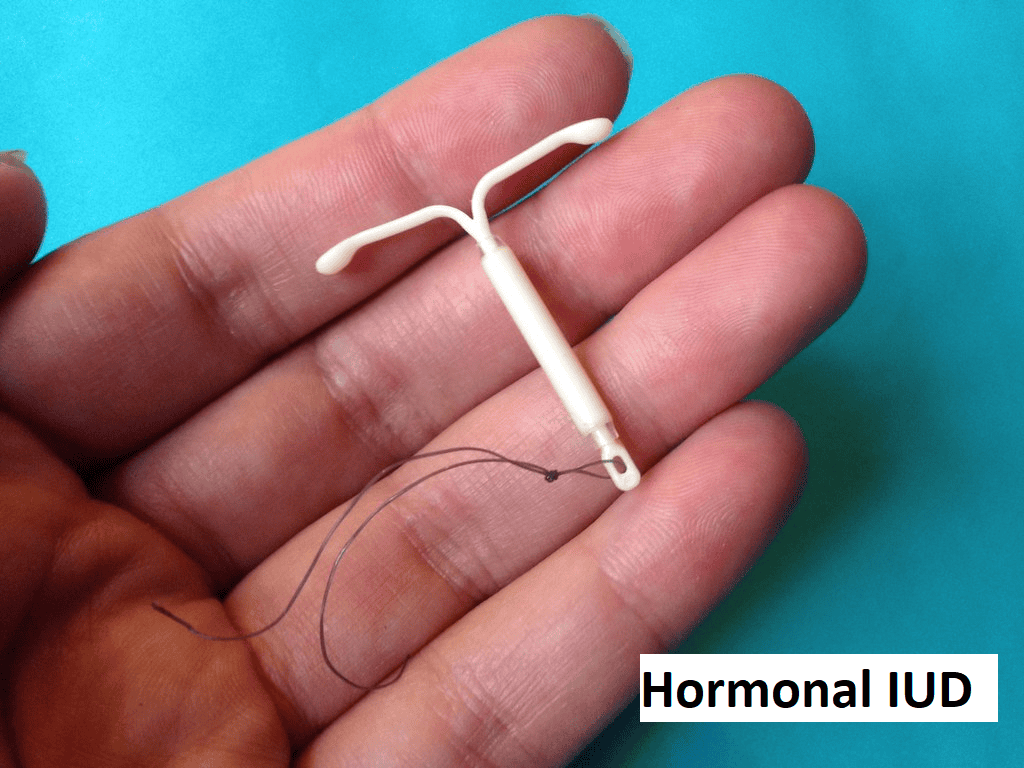
An intrauterine device (IUD) is a type of birth control device that is inserted into the uterine cavity and provides long-term and reversible contraception. It usually comes in a small T-shaped device made of flexible plastic, generally measuring between 2 to 3 cm in width and length. This type of birth control is highly effective and convenient. The doctor puts the ІUD in your uterus by going through your vagina and cervix, either in the outpatient clinic setting or under anaesthesia in the operating theatre as per individual case requirements.
Different types of IUD
There are 2 types of IUD commonly available and widely used in the world
- Copper IUD – the T-shaped device has a copper wire coil wrapped around it. The copper acts as a spermicide (creating a toxic environment and disrupting the sperm’s ability to fertilise the egg in the uterus). It can cause changes in the uterine lining, making it less suitable for implantation. It is effective immediately after insertion. It can also be used as emergency contraception and can prevent pregnancy if inserted within five days of unprotected sex.
2. Hormonal IUD – it has a similar shape to the copper IUD but instead of copper, it contains a hormone reservoir that releases a small amount of progestogen, a synthetic hormone similar to natural progesterone. This hormone has effects on the cervical mucus, making it thicker and able to prevent the sperm from reaching the egg. It can cause thinning of the inner uterine layers, making it less likely for a fertilised egg to implant. There are several brands of hormonal IUD in the world, such as Mirena, Kyleena, Liletta, and Skyla. These can last between 3 to 7 years, depending on the brand. Many women who had a hormonal IUD inserted are likely to have lighter, less painful periods due to the thinned-out inner uterine lining. Some women will not get periods at all. The reduction or absence of period is not harmful. This is beneficial in those with heavy menstrual bleeding, severe period pain or those with certain gynaecological disorders. The menstrual periods or fertility will usually return to normal soon after removal.
Benefits of using IUD (copper or hormonal)
• Highly Effective: one of the most reliable forms of birth control, with more than 99% effective at preventing pregnancy,
• Long-term protection: Depending on the type, an IUD can provide protection for 3 to 10 years.
• Low Maintenance: convenient and does not require any further action to ensure effectiveness
• Reversible: does not affect future fertility and fertility returns quickly upon removal.
• Cost-Effective: the long-term costs are much lower compared to other methods of contraception.
• Non-Hormonal Option: The copper IUD provides a hormone-free method of birth control
• Hormonal type – significant reduction in menstrual flow and pain. Recommended for the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding and certain gynaecological disorders such as adenomyosis or endometriosis.
What are the risks and disadvantages of an IUD?
- Compared to condoms, an ΙUD does not protect you against sexually transmitted infections. If you are worried about this, the condom will be a better option.
- The IUD may be spontaneously expelled during your period, especially if the flow is heavy and usually occurs during the first few months
- The insertion and removal must be performed by a medically trained staff member.
- During insertion, there is a small risk of perforation of the uterine wall, and there may be bleeding and pain. It can be a serious complication that may require surgical intervention
- There is a risk of infection during insertion. However, the risk is small and usually occurs within the first few weeks after insertion.
- There may be changes in menstrual cycles – the hormonal IUD may cause irregular light bleeding or spotting, especially in the first few months. The copper IUD may cause menses to be heavier and painful.
It is important to discuss these effects with your healthcare provider to decide if this is a suitable option for you and will help you make an informed decision.
Who Can Use an IUD?
Most women can use an IUD safely. Prior to insertion, your healthcare provider will assess your suitability and discuss available options for you. IUD may not be suitable for you if you have the following conditions:
- Current or suspected infection of the pelvis or vagina, especially sexually transmitted infections.
- Unexplained vaginal bleeding
- Abnormal uterus structure or fibroids that interfere with the placement of the IUD
- Allergy to copper (for the copper IUD)
- Previous ectopic pregnancy
What to expect during the insertion?
- It is a relatively quick and straightforward procedure performed in the clinic.
- Preparation: your healthcare provider will perform a pelvic exam to assess the position and size of your uterus. If there is the presence of abnormal discharge or suspected infections, the test may be done to exclude infections and the insertion deferred.
- In some situations, oral painkiller medication may be given 30 minutes prior to insertion to reduce pain and discomfort.
- The IUD is inserted through the cervix into the uterus using a special applicator. You may experience some cramping or discomfort during the procedure.
- There is usually some spotting or cramping for a few days after insertion. For hormonal IUD, the spotting may persist a little longer and can be irregular for several weeks.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers for a few days can help manage any discomfort.
Post insertion care
- There is a short thread that hangs out of the cervix (usually 2 to 3 cm). You can feel for this thread regularly to ensure the IUD is still in place, although this is not really necessary.
- Be aware of complications associated with IUD use and see your healthcare provider if you have – severe pain, abnormal vaginal discharge, heavy bleeding, fever, or any other unusual symptoms.
- Attend the follow-up appointments, which is typically a few weeks after insertion, to check the IUD’s position and address any concerns.
- The IUD can be seen easily in the uterus via an ultrasound scan.
- You should take note of the removal date. The removal of the IUD is a simple procedure and is performed in the clinic.

You should consult your healthcare provider immediately if you have the following:
- Inability to feel the IUD string, or if the string feels longer than usual
- Severe abdominal or pelvic pain
- Abnormal per vaginal bleeding – either heavy or prolonged
- Fever or chills, which may suggest infection
- Unusual vaginal discharge
- Painful intercourse
- Suspected pregnancy
To subscribe to the free newsletter to get the latest updates on Women’s Health, click HERE.

 This article will help you to prepare the essential items that you need to bring to the hospital for your labour and delivery. The preparation should be done when you are about eight months pregnant. Pack the items listed in the list below in a bag and place the bag in a convenient place that is easy for you or your spouse to retrieve it when needed.
This article will help you to prepare the essential items that you need to bring to the hospital for your labour and delivery. The preparation should be done when you are about eight months pregnant. Pack the items listed in the list below in a bag and place the bag in a convenient place that is easy for you or your spouse to retrieve it when needed.