The main purpose of contraception (or birth control) is to prevent an unplanned pregnancy. You should know and understand the different types of methods available to you, the risks and benefits of each, and any possible side effects so that both you and your partner can able to make an informed choice. Contraception can be broadly divided into:
The main purpose of contraception (or birth control) is to prevent an unplanned pregnancy. You should know and understand the different types of methods available to you, the risks and benefits of each, and any possible side effects so that both you and your partner can able to make an informed choice. Contraception can be broadly divided into:
- Temporary or permanent methods – permanent birth control is accomplished through sterilization (tying or removal of the fallopian tubes) or hysterectomy (removal of womb/uterus). The rest of the methods are classified as temporary or reversible.
- Short term or long-term methods – short term methods are condoms and oral pills. Long term methods are injectables, intrauterine device and hormonal implants.
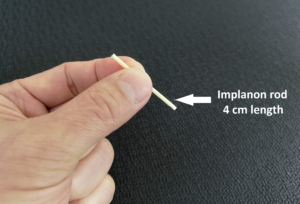 Hormone implant currently available is Implanon NXT®. It consists of a single plastic rod measuring 4 cm and contain a progestogen hormone called etonogestrel. Implanon is inserted surgically, just under the skin of the upper arm. The implant will release a minute amount of this hormone every day for 3 years. It works by preventing the monthly ovulation (the release of an egg from the ovary) during your menstrual cycle. It also thickens the vaginal mucus to prevent sperm from reaching the egg (fertilization). Continuous effect of the hormone will thin out the lining of the uterus (womb) to prevent attachment of a fertilized egg. Implanon does not contain any oestrogen.
Hormone implant currently available is Implanon NXT®. It consists of a single plastic rod measuring 4 cm and contain a progestogen hormone called etonogestrel. Implanon is inserted surgically, just under the skin of the upper arm. The implant will release a minute amount of this hormone every day for 3 years. It works by preventing the monthly ovulation (the release of an egg from the ovary) during your menstrual cycle. It also thickens the vaginal mucus to prevent sperm from reaching the egg (fertilization). Continuous effect of the hormone will thin out the lining of the uterus (womb) to prevent attachment of a fertilized egg. Implanon does not contain any oestrogen.
Advantages
- It is highly effective for contraceptive use (more than 99% effective at preventing pregnancy).
- The hormone used in the implants is a progestogen and is a good option for women who cannot take oestrogen hormones that are used in the oral combined oral contraceptives pills.

- Some women may develop scanty menses or no menstrual bleeding at all. This is an advantage and ideal for women with prior period pain or heavy menstrual bleeding.
- It requires no daily routine.
- Can be used while you are still breastfeeding.
- Provides enjoyment of spontaneous sexual intercourse; no need to worry once it is inserted
It is reversible and can be removed at any time. Fertility will return once it is removed.
Disadvantages
- Implanon insertion requires a minor surgical procedure with a local anaesthetic injection.
- A small few mm scar may be visible.
- Side effects from the implants include irregular menstrual cycles with unpredictable bleeding, headaches, depression, breast pain, ovarian cysts, acne and weight gain. The side effects are minor and tend to diminish with time.
- Does not protect against sexually transmitted infection. A form of barrier protection (condoms) will need to be used.
Insertion
The usual recommendation is to insert it during the menses (days 1–5 of menses). Insertion during this time ensures that you are not pregnant, and the implant is effective immediately. It can also be inserted at any time, provided that pregnancy has been ruled out prior to insertion. However, it will not be effective for the first seven days and an additional contraceptive method must be used for at least 7 days before the implant starts to work.
The insertion procedure will take about 10 to 15 minutes in the clinic. A local anaesthetic is injected into the upper arm to numb the area for placement. This injection may cause some stinging pain. However, the insertion is painless once the anaesthetic takes effect. The implant comes pre-loaded in a special applicator and the applicator needle will be injected underneath the skin to place the implant. The presence of the implant should be verified by feeling it (palpation) immediately following insertion. A correctly placed implant should be easily felt. A small adhesive bandage will be placed over the insertion site and the area covered with a pressure bandage to minimise bruising. You may remove the pressure bandage on the following day. You should not worry if you have slight pain and see some bruises around the insertion site. It will disappear after a few days.
Removal
Implants must be removed after three years. They can also be removed earlier if you wish (either because you wish to get pregnant again or due to some side effects). To remove the implant, your doctor will first numb your arm with a local anaesthetic injection similar to the process during insertion. A small incision will be made over the tip of the implant and the implant will be pull out with a small forcep. If you wish, another new implant can be inserted at the same time. If you choose not to get a new implant, only an adhesive bandage will be applied (without the need for pressure bandage) and you must use another form of contraception to prevent pregnancy.
Contra-indications
Certain conditions may not allow the use of the implant or deem it unsuitable due to a higher risks. These are:
- A history of breast cancer.
- Unexplained vaginal bleeding (this needs to be investigated first to ascertain the cause or diagnosis).
- If you have a thrombosis – it refers to the formation of a blood clot in a blood vessel such as in the legs (deep venous thrombosis) or the lungs (pulmonary embolism).
- History of heart attack or a stroke.
- Presence of liver tumour or liver disease.
 Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding
Implanon can be used while you are breast-feeding. Although a small minute amount of the hormone passes over into the breast milk, there is no effect on the production or the quality of breast milk, nor on the growth and development of the child.
Post-insertion follow-up
You may ask you to return for a (routine) medical check-up sometime after insertion of the implant. The frequency and nature of further check-ups will depend on your personal situation. You should keep a diary of your menstrual pattern (menstrual calendar) and discuss the pattern with your doctor on your next follow up visit.
 See your doctor immediately if there:
See your doctor immediately if there:
- you have unusual, heavy and prolonged vaginal bleeding with dizziness, lethargy, shortness of breath or pale looking skin.
- significant side effects that are troubling you.
- suspect that you are pregnant.
- the implant is not palpable at any time.
To print a pdf copy, click HERE
To watch a video on Implanon insertion, CLICK HERE
[mailerlite_form form_id=3]