Hysterectomy is the surgical removal of the uterus (womb) resulting in inability to become pregnant and immediate cessation of menstruation. It is a common operation and may involve removal of the cervix, ovaries and fallopian tubes at the same time.
Please discuss all aspects of this surgical procedure, its risks and benefits, and any possible alternative therapies. Your health care provider will help you decide which type of hysterectomy is appropriate for you, depending on your indications for surgery and your medical history.
News
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
 Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) refers to a spectrum of clinical problems due to hormonal and metabolic imbalance, which can affect the reproductive and endocrine systems.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) refers to a spectrum of clinical problems due to hormonal and metabolic imbalance, which can affect the reproductive and endocrine systems.
How Common?
PCOS affects 5-10% of all women of childbearing age regardless of race or nationality. It may begin during puberty and become more severe with time.
Hysteroscopy (diagnostic and operative)
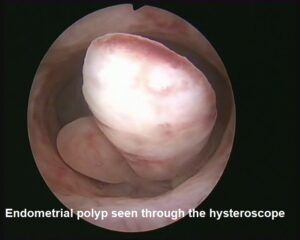

Reasons for the procedure
- Evaluation and treatment of abnormal uterine bleeding.


- To look for the displaced and removal of the intrauterine device (IUD).
- Evaluation for infertility (difficulty in conceiving) or recurrent miscarriage.
- Uterine polyps, fibroids or adhesions (which is called Ashermann’s syndrome).
- Obstructed fallopian tubes.
- Congenital malformations of the uterus
Anaesthesia and Analgesia in Obstetrics and Gynaecology


That day is remembered as a milestone in anaesthesia and celebrated as World Anaesthesia Day.
From that date onward, many progresses have been made in the field of anaesthesia, and more so specifically for the practice of obstetrics and gynaecology.
On the 16th August 1897, a German surgeon by the name of Dr. August Bier administered the first spinal anaesthetic. 

Suction evacuation for miscarriage

Reasons for procedure
Miscarriage


How common is it?
Combined oral contraceptives (COC) pills


Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia (CIN)
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (or CIN) refers to the presence of abnormal cells seen on the cervical cytology smear. These abnormal cells are obtained from the lining of the outer cervix and can range from mild to severe changes. A diagnosis of CIN changes is not cancer. However, the severe form of dysplasia can be considered a precancerous condition and may eventually progress to cancer in several years if not treated.
The cervical cytology smear was previously referred to as Pap smear. Currently, the newer cervical cancer screening uses a liquid based cytology and the commonest one used are: Thin Prep or Sure-Path. These are better and more accurate compared to the conventional Pap smear test.