 Genital herpes is a viral infection of the genitals. It is transmitted by sexual activity such as intercourse or oral sex and can affect both sexes (man and woman). Genital herpes is often associated with other sexually transmitted infections. It is an infection caused by the herpes simplex virus or HSV. There are two types of HSV and both can cause genital herpes. HSV type 1 most commonly infects the lips, causing sores, but it also can infect the genital area. HSV type 2 is the usual cause of genital herpes but can also infect the mouth during oral sex. The lesions can occur in and around the vaginal area, on the penis, around the anal opening, and on the buttocks or thighs. Occasionally, sores also appear on other parts of the body where the virus has entered through broken skin.
Genital herpes is a viral infection of the genitals. It is transmitted by sexual activity such as intercourse or oral sex and can affect both sexes (man and woman). Genital herpes is often associated with other sexually transmitted infections. It is an infection caused by the herpes simplex virus or HSV. There are two types of HSV and both can cause genital herpes. HSV type 1 most commonly infects the lips, causing sores, but it also can infect the genital area. HSV type 2 is the usual cause of genital herpes but can also infect the mouth during oral sex. The lesions can occur in and around the vaginal area, on the penis, around the anal opening, and on the buttocks or thighs. Occasionally, sores also appear on other parts of the body where the virus has entered through broken skin.
Gynaecology
What you need to know about Urodynamic Studies
 What is this test?
What is this test?
This is a test to assess bladder function and will involve the evaluation of the bladder during the filling, storing and emptying of the urine.
Why is it needed?
This test will provide information about your urinary problems and may help identify the cause. This will also help the doctor in choosing the best therapy for you.
How to prepare for the test?
 You may eat or drink or take your regular prescribed medications prior to the test. The test is performed with a full bladder. There is no need to empty your bladder just before the test unless instructed by the nurse. Inform the nurse if you are unable to hold your full bladder any longer while waiting for your turn. The test can be done even if you are having your period unless it is very heavy on the day of the test. Please discuss this with your doctor. Please be punctual.
You may eat or drink or take your regular prescribed medications prior to the test. The test is performed with a full bladder. There is no need to empty your bladder just before the test unless instructed by the nurse. Inform the nurse if you are unable to hold your full bladder any longer while waiting for your turn. The test can be done even if you are having your period unless it is very heavy on the day of the test. Please discuss this with your doctor. Please be punctual.
Post-menopausal bleeding


Symptoms and signs
- Vaginal bleeding, which may be a light-brown discharge or heavy, red bleeding (with or without clots). Mucus may accompany the bleeding. Bleeding episodes may vary in length.
- Women who are on hormonal replacement therapy may have some bleeding and this can be normal, depending on the type of hormone that she is taking. Please consult your doctor about the types of bleeding to be concerned about.
- Presence of excessive bleeding, progressive abdominal distention, pain and feeling
unwell usually signify a more serious problem.
Menopausal Hormone Therapy (MHT)

Menopause – symptoms and treatment options


Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure (LEEP/LLETZ) for CIN
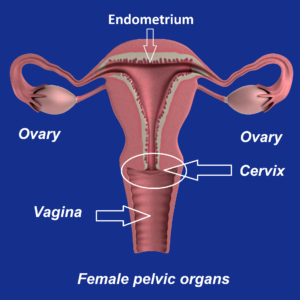

Reason for the procedure
• Presence of CIN lesions from the colposcopy evaluation and confirmed via cervical biopsy. Some types of CIN can progress to cervical cancer if not treated. This can be used as a treatment for CIN lesions.
• Unsatisfactory colposcopic evaluation whereby the whole transformation zone cannot be visualized or the cervix appeared abnormal and requires a bigger tissue specimen for a more accurate diagnosis to exclude cancer changes.
Endometrial biopsy (Endometrial sampling or curettage)
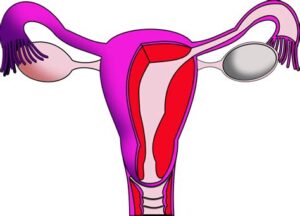

Reason for the procedure
It is done to diagnose endometrial cancer or hyperplasia (with or without atypia). Endometrial hyperplasia is a potentially precancerous condition. This procedure is indicated in a woman with abnormal uterine bleeding. This includes bleeding between menstrual periods, excessive bleeding during a menstrual period, or bleeding after menopause. It is also done to exclude endometrial cancer in post-menopausal women with abnormal endometrial finding on ultrasound scan of the uterus.
Vasectomy – Male contraception
Article contributed by Dr Peter Ng and Dr Beatrice Chua Yoong Ni

Vasectomy is the contraception of choice for 6%–8% of married couples worldwide. Vasectomy is a minor procedure that provides effective and permanent contraception. In fact, it is far more effective than many other methods of contraception, including female sterilization.