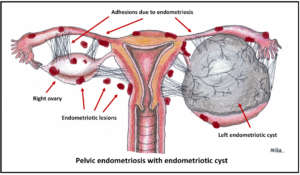
 Endometriosis is a condition whereby tissues from the lining (endometrium) of the uterus becomes implanted in areas outside the uterus such as the outer surface of the uterus, the fallopian tubes or the ovaries. Rarely, the endometrial tissue may spread beyond the reproductive organs and pelvic region.
Endometriosis is a condition whereby tissues from the lining (endometrium) of the uterus becomes implanted in areas outside the uterus such as the outer surface of the uterus, the fallopian tubes or the ovaries. Rarely, the endometrial tissue may spread beyond the reproductive organs and pelvic region.
In a normal menstrual cycle, the endometrial tissues respond to cyclical female hormones and becomes progressively thicker and will eventually shed each month if the woman is not pregnant. It is discharged as menstrual flow at the end of each cycle. In endometriosis, this shedding and bleeding will occur outside the uterus as well, causing significant pain. Recurrent bleeding and healing cycle will eventually cause scar tissue formation and destruction of pelvic structures. The excessive blood will accumulate over a period of time and eventually forms a cyst in the ovary (called endometriotic cyst or endometrioma). The 4 stages (classification) of endometriosis (minimal, mild, moderate or severe) are used to describe the location and the severity of the disorder.